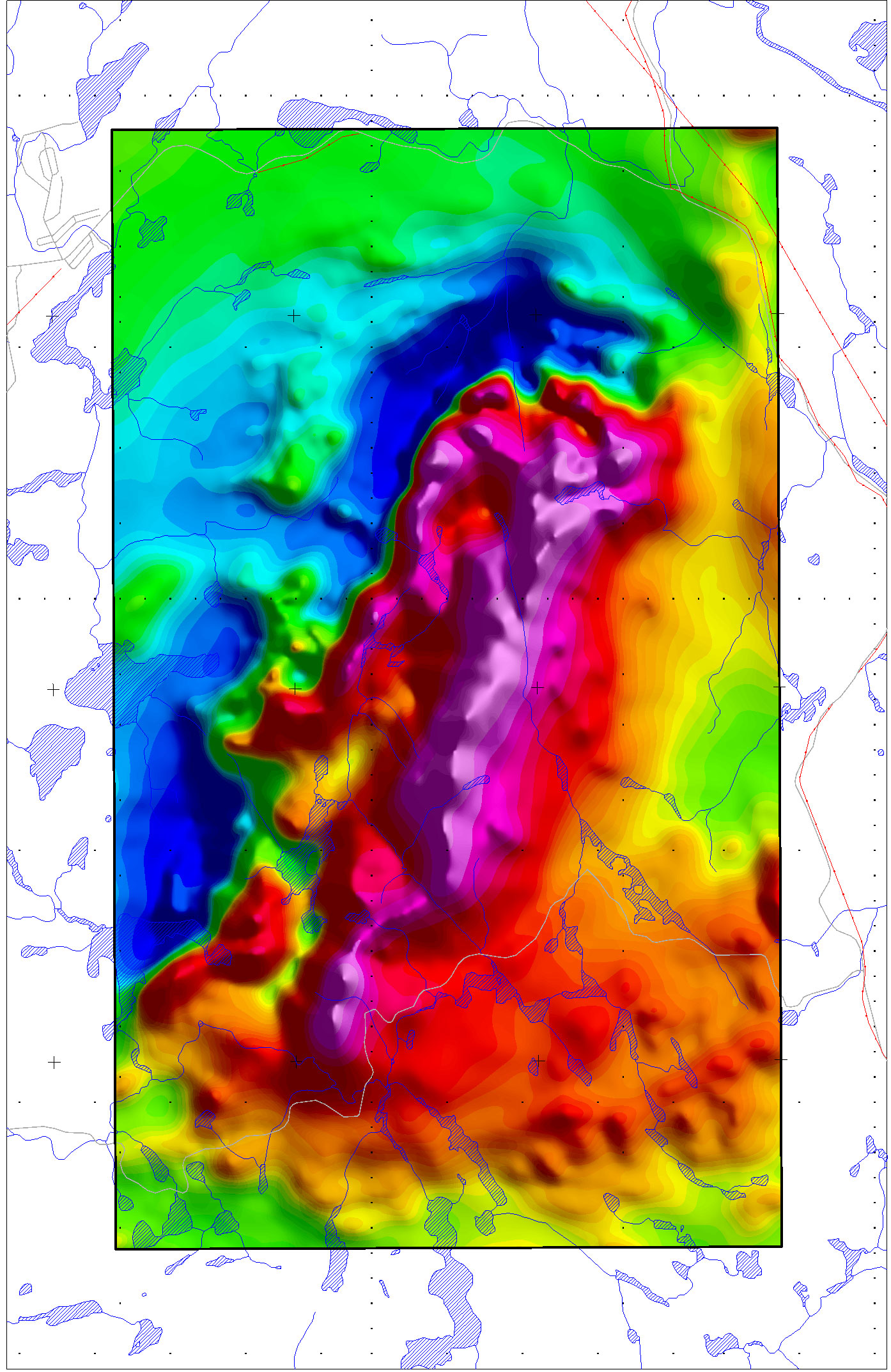
Airborne magnetometry through an onboard magnetometer installed in the tail stinger and / or at the end of wing tips, is used to detect magnetic anomalies of the local terrestrial magnetic field.
The anomalies may be an indication of concentrations of ferromagnetic minerals in the Earth's crust, and may be used to visualize the geological structure of the upper crust in the subsurface, particularly the spatial geometry of bodies of rock and the presence of faults and folds. This is a particularly useful tool for geological mapping in areas where bedrock is obscured by overburden or water.
The main challenge is to remove the influence of the magnetic field caused by the plane, on the data measured by magnetometers. To do this, a fluxgate magnetometer three (3) axes Barrington is mounted at the base of each magnetometer. The two fluxgate magnetometers measure the direction and magnetic field variation rate of the aircraft at the base of each magnetometer relative to the magnetic field of the Earth. The correction coefficients are then calculated from a figure of merit (FOM) to enable real-time compensation using the magnetic compensator ARC500 RMS. A compensation is also possible to post using software developed for this purpose.
For more information, please contact our Airborne Survey Team